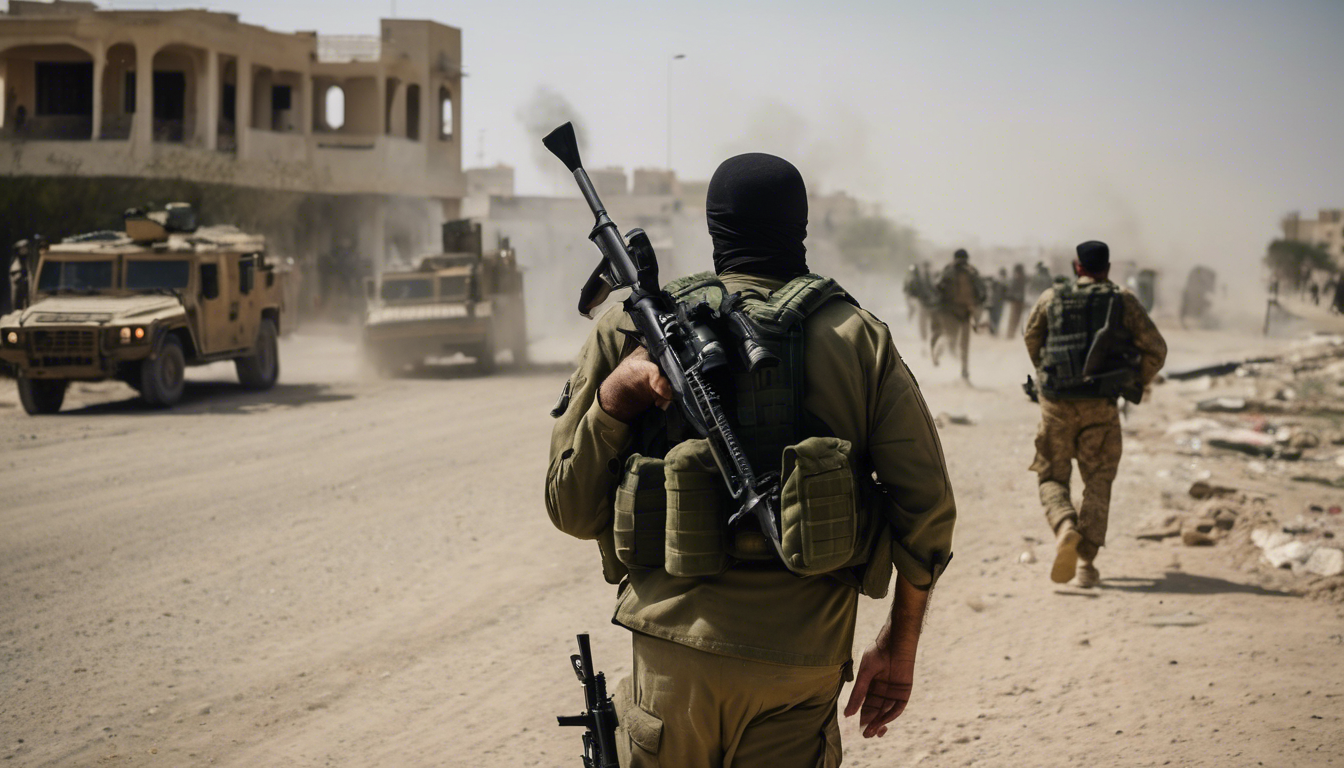
Hamas has officially rejected the latest mediator-backed ceasefire proposal, insisting on the full release of all Israeli hostages in return for any agreement. The move comes amidst Israel’s ongoing Gaza offensive and growing international pressure.
Background
Hamas captured three Israeli soldiers and killed 12 civilians in an attack on October 7, 2023, triggering a large-scale military response from Israel. The conflict has resulted in significant civilian casualties, widespread destruction, and a humanitarian crisis in Gaza.
The conflict has deep historical roots, rooted in the long-standing Israeli-Palestinian struggle over land and statehood. Hamas, a Sunni-Islamic fundamentalist organization, controls the Gaza Strip and rejects Israel’s right to exist.
Previous attempts to negotiate a ceasefire have often been frustrated by both parties’ intransigence, leading to cycles of violence and renewed hostilities.
Key Developments

Hamas, through senior official Izzat al-Rishq, reaffirmed its willingness to accept a comprehensive deal that includes the release of all prisoners in exchange for a negotiated settlement of its own hostages. However, this proposal was met with resistance from Israel.
- Hamas accuses Netanyahu of blocking progress on the ceasefire.
- President Trump insists on the immediate return of all hostages.
- Egypt and Qatar, as mediators, express frustration with Israel.
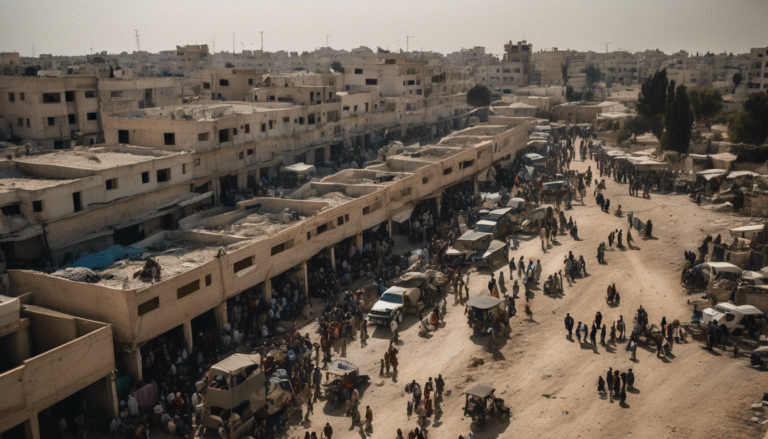
- The WHO declares famine has set in Gaza, affecting more than half a million people.
Israel’s Prime Minister Netanyahu rejects Hamas’ August 18 ceasefire offer, citing concerns that it did not ensure the safety of all hostages. Despite growing international condemnation, including from Europe, Israel continues its offensive in Gaza.
Industry/Market Context
The Gaza conflict impacts the broader Middle Eastern geopolitics, influencing regional trade, investment flows, and diplomatic relations. International donors, including the United Nations, have struggled to provide adequate aid due to the violence and blockades.
The crisis also affects the energy sector, with the disruption of power lines and pipelines impacting electricity supply and economic activities in Gaza and surrounding areas.
Tensions between Hamas and Fatah, the other major Palestinian faction, remain high, adding another layer of complexity to any potential resolution. This intra-Palestinian rivalry influences how international actors perceive and mediate the conflict.
Implications & Risks
Continued hostilities risk exacerbating the humanitarian crisis in Gaza, potentially resulting in mass casualties and further destabilizing the region. The conflict may also strain international relations, particularly between countries supporting Israel and those advocating for Palestinian rights.
The conflict’s impact extends beyond Palestine. Regional stability is crucial for global energy markets and trade routes. Increased tension could lead to higher oil prices and supply chain disruptions.
The crisis has significant implications for international law, raising questions about the legality of prolonged blockades, military actions, and the treatment of civilians in conflict zones.
What’s Next
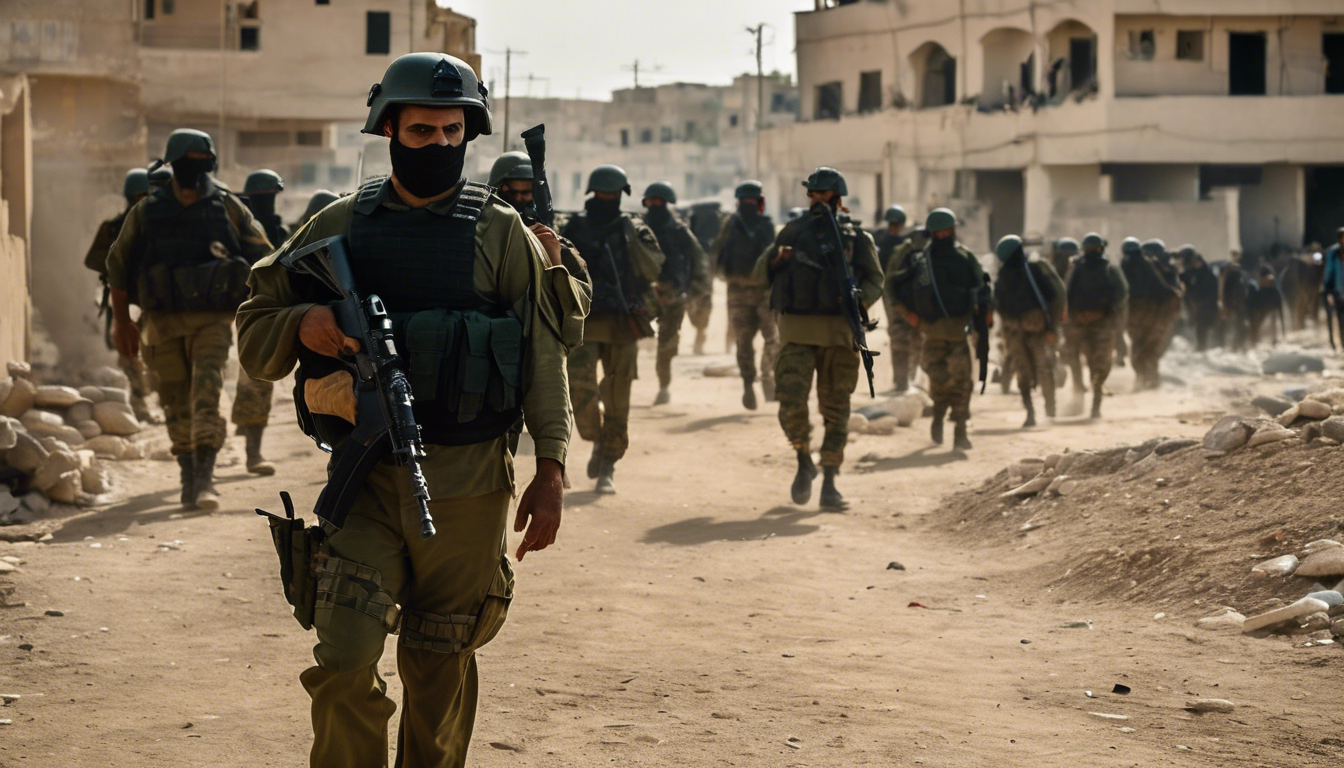

The upcoming days and weeks will likely see continued military operations in Gaza, with increased international pressure on both Hamas and Israel to reach a ceasefire agreement. Mediators may seek new avenues to facilitate negotiations and address the core issues of the conflict.
Humanitarian organizations will continue to struggle to provide assistance due to access restrictions, potentially exacerbating the food crisis and healthcare needs of Gazans.
Political leaders in Israel and Palestinian territories may face internal pressures to find a solution, with international public and political opinion increasingly favoring a resolution that protects civilian life and addresses underlying grievances.
The evolving conflict may force a reevaluation of existing diplomatic strategies and potentially open new avenues for peace negotiations, though the path forward remains uncertain.